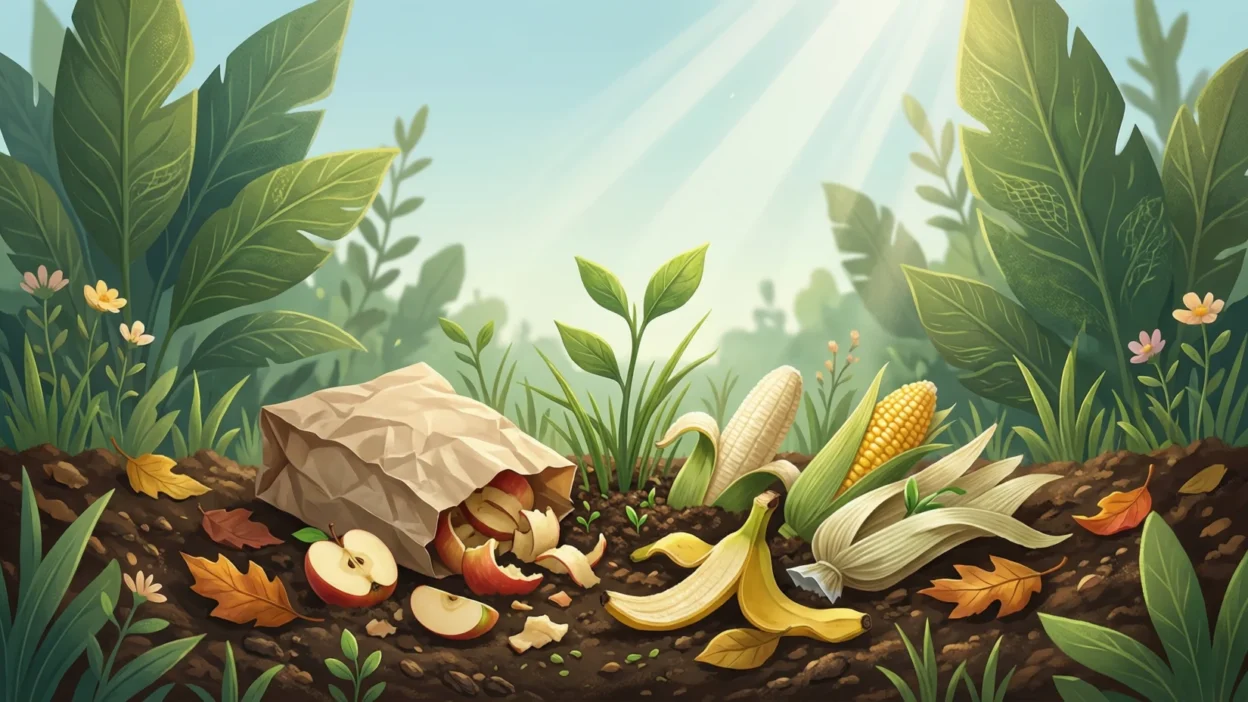
Biodegradable is a word we hear every day. It is used for bags, plates, and packaging. Many people see this word on products but do not fully understand it.
Biodegradable is important for our planet. It helps reduce waste and pollution. Learning this word helps us make better choices for the environment.
This article explains biodegradable in a very simple way. You will learn its meaning, examples, benefits, and limits.
What Does Biodegradable Mean?
Biodegradable means something can break down naturally. It breaks down over time. Nature helps in this process.
When an item is biodegradable, tiny living things eat it. These tiny living things are called microorganisms. They turn waste into natural matter.
Biodegradable items do not stay forever. They return to the earth safely.
Simple Definition of Biodegradable
Biodegradable means able to break down naturally by living organisms.
It becomes part of soil, water, or air. It does not harm nature when it breaks down fully.
How Biodegradable Materials Break Down
Biodegradable materials break down step by step. This process is slow or fast depending on conditions.
Heat, air, and water help the process. Living organisms also help.
Over time, the material changes. It becomes simple and natural again.
What Is Decomposition?
Decomposition means breaking down. It is a natural process.
Leaves fall from trees. They rot and turn into soil. This is decomposition.
Biodegradable items follow the same process.
Role of Microorganisms in Biodegradation
Microorganisms are very small living things. We cannot see them with our eyes.
They include:
- Bacteria
- Fungi
These organisms eat waste. They use it as food. This helps waste break down.
Role of Bacteria
Bacteria live in soil, water, and air. They eat organic matter.
They break big waste into small parts. This helps nature recycle waste.
Role of Fungi
Fungi include molds and mushrooms. They help break hard materials.
They are important for wood, paper, and plant waste.
What Is Organic Matter?
Organic matter comes from plants and animals.
Examples include:
- Food waste
- Paper
- Leaves
- Wood
Organic matter is usually biodegradable.
Aerobic and Anaerobic Decomposition
There are two main types of decomposition.
Aerobic Decomposition
This happens with oxygen.
It is fast and smells less.
Anaerobic Decomposition
This happens without oxygen.
It is slow and may smell bad.
Both help break biodegradable waste.
Examples of Biodegradable Materials
Many daily items are biodegradable.
Common examples include:
- Food scraps
- Fruit peels
- Paper
- Cardboard
- Cotton cloth
- Leaves
These items break down naturally.
Food Waste as Biodegradable Material
Food waste is one of the best examples.
Examples:
- Vegetable peels
- Leftover rice
- Bread
- Fruits
Food waste breaks down quickly and helps soil.
Paper and Paper Products
Paper comes from trees. It is biodegradable.
Examples include:
- Newspapers
- Paper bags
- Cardboard boxes
Paper breaks down faster than plastic.
Natural Fibers and Biodegradability
Natural fibers come from plants or animals.
Examples:
- Cotton
- Wool
- Jute
These fibers are biodegradable and eco-friendly.
What Is Biodegradable Plastic?
Biodegradable plastic is different from normal plastic.
It is made from plant materials. It can break down with help from nature.
However, it still needs special conditions to break down fully.
Biodegradable vs Non-Biodegradable Materials
Biodegradable Materials
- Break down naturally
- Less harmful to the environment
- Return to soil
Non-Biodegradable Materials
- Do not break down easily
- Stay for many years
- Cause pollution
Plastic bottles and glass are non-biodegradable.
How Long Do Biodegradable Materials Take to Break Down?
The time depends on many things.
Some items break down in weeks. Others take months or years.
Examples:
- Food waste: few weeks
- Paper: few months
- Wood: many years
Conditions like heat and water matter.
Biodegradable vs Compostable
Many people confuse these words.
Biodegradable
- Breaks down naturally
- May take long
- No special place needed
Compostable
- Breaks down into compost
- Needs special conditions
- Helps soil health
All compostable items are biodegradable. But not all biodegradable items are compostable.
Composting and Biodegradable Waste
Composting is a natural recycling process.
It turns organic waste into rich soil. This soil helps plants grow.
Biodegradable waste is perfect for composting.
Benefits of Biodegradable Materials
Biodegradable materials are good for many reasons.
Main benefits include:
- Less pollution
- Cleaner environment
- Better soil health
- Reduced landfill waste
They help protect nature.
Biodegradable Materials and Pollution Reduction
Non-biodegradable waste causes pollution.
Biodegradable waste breaks down and disappears.
This reduces land, air, and water pollution.
Impact on Landfills
Landfills are places where waste is dumped.
Biodegradable waste breaks down in landfills. Non-biodegradable waste stays for years.
Using biodegradable products helps reduce landfill size.
Biodegradable Materials in Daily Life
We use biodegradable items every day.
Examples include:
- Food
- Paper towels
- Wooden items
- Cotton clothes
Choosing these items helps the planet.
Biodegradable Products in Packaging Industry
Many companies now use biodegradable packaging.
Examples:
- Paper bags
- Cardboard boxes
- Plant-based wraps
This reduces plastic waste.
Role of Biodegradable Materials in Agriculture
Farmers use biodegradable materials often.
Examples include:
- Organic fertilizers
- Plant waste compost
These materials improve soil health.
Are All Natural Materials Biodegradable?
Most natural materials are biodegradable. But not all break down easily.
Examples:
- Wood takes long
- Some treated fabrics do not break down
Natural does not always mean fast biodegradable.
Limitations of Biodegradable Materials
Biodegradable materials also have limits.
Some problems include:
- Need proper conditions
- Take time to break down
- Can still cause harm if misused
They are helpful but not perfect.
Misleading Labels on Biodegradable Products
Some products say “biodegradable” but are not fully safe.
They may need special factories to break down.
Always check labels carefully.
Environmental Impact of Biodegradable Products
Biodegradable products help the environment when used correctly.
They support:
- Environmental sustainability
- Waste reduction
- Ecosystem balance
But proper disposal is important.
Biodegradable Materials and Ecosystems
Ecosystems are communities of plants and animals.
Biodegradable waste supports ecosystems by returning nutrients to soil.
This helps plants grow and animals survive.
Waste Management and Biodegradable Waste
Good waste management is important.
Biodegradable waste should be:
- Separated
- Composted
- Recycled naturally
This keeps cities clean.
Role of Biodegradable Materials in Sustainability
Sustainability means using resources wisely.
Biodegradable materials help by:
- Reducing waste
- Saving natural resources
- Protecting future generations
They support a greener future.
How to Identify Biodegradable Products
Look for:
- Eco-friendly labels
- Compostable marks
- Plant-based materials
Avoid plastic when possible.
Simple Tips to Live a Biodegradable Lifestyle
You can help the planet easily.
Simple steps:
- Use paper bags
- Compost food waste
- Avoid single-use plastic
- Choose natural products
Small changes make a big difference.
Myths About Biodegradable Materials
Myth 1: All biodegradable items break down fast
Truth: Some take years.
Myth 2: Biodegradable means harmless
Truth: Disposal still matters.
Future of Biodegradable Materials
Scientists are creating better materials.
Future goals include:
- Faster decomposition
- Strong biodegradable plastics
- Lower cost products
This will help the planet more.
Importance of Learning About Biodegradable Materials
Understanding biodegradable helps us make smart choices.
It teaches responsibility toward nature.
Education is the first step toward change.
Conclusion
Biodegradable means breaking down naturally. It helps reduce waste and pollution. Biodegradable materials protect soil, water, and air. They support a healthy environment. By choosing biodegradable products, we help our planet. Every small step counts. A cleaner and greener future starts with us.
FAQs
❓ What does biodegradable mean?
Biodegradable means a material can break down naturally by bacteria and fungi without harming the environment.
❓ What are examples of biodegradable materials?
Food waste, paper, cardboard, cotton, leaves, and wood are common biodegradable materials.
❓ Is biodegradable better than plastic?
Yes, biodegradable materials break down naturally, while plastic stays in the environment for many years.
❓ How long does biodegradable waste take to decompose?
It depends on the material. Food waste may take weeks, while wood can take years.
❓ Are biodegradable and compostable the same?
No. All compostable items are biodegradable, but not all biodegradable items are compostable.

Jack London is a versatile writer with a strong ability to explain ideas in a clear and engaging way.
He focuses on creating informative, easy-to-understand content for a wide range of readers.
Jack London currently writes helpful articles for repliesnest.com, delivering trustworthy and reader-friendly information.